When it comes to single-board computers (SBCs), there are two names that come to mind: ODROID and Raspberry Pi. These two brands are highly popular among tech enthusiasts, hobbyists, and developers. In this article, we will be comparing the ODROID-N2+ and the Raspberry Pi 4, two of the most powerful SBCs currently available in the market. We will be looking at their features, performance, and price to help you decide which one is the right fit for your needs.
ODROID-N2+ Overview
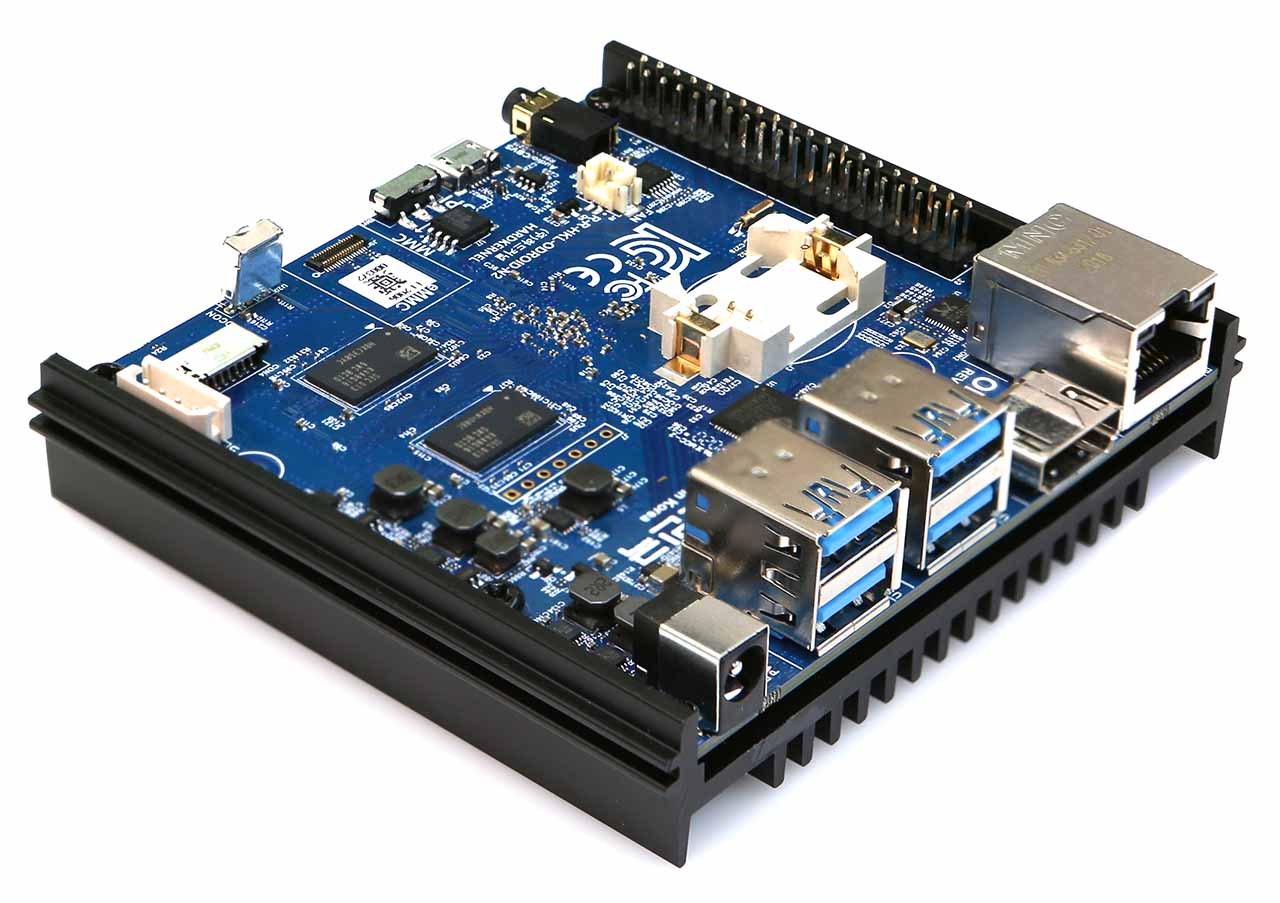
Odroid N2+
The ODROID-N2+ is a single-board computer that was released in 2020 by the Korean company Hardkernel. It is an upgrade to the original ODROID-N2 and features a powerful Amlogic S922X processor, which is a 64-bit Arm Cortex-A73/A53 CPU with a Mali-G52 GPU. It comes with 4GB or 2GB of DDR4 RAM and has eMMC storage options of 32GB, 64GB, or 128GB. It also features Gigabit Ethernet, USB 3.0, and an HDMI 2.0 port.
Raspberry Pi 4 Overview
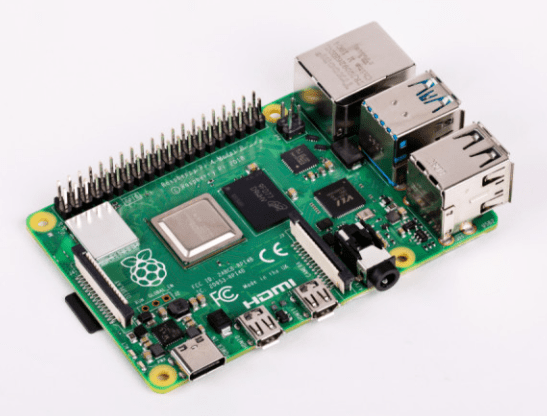

Raspberry Pi 4
The Raspberry Pi 4 is the latest iteration of the popular Raspberry Pi line of SBCs. It was released in 2019 and features a powerful Broadcom BCM2711 quad-core Cortex-A72 (ARM v8) 64-bit SoC with a VideoCore VI GPU. It comes with 2GB, 4GB, or 8GB of LPDDR4-3200 SDRAM and has microSD storage options. It also features Gigabit Ethernet, USB 3.0, and two micro-HDMI ports.
1. Performance
The ODROID-N2+ is powered by an Amlogic S922X processor, which is a powerful ARM Cortex-A73/A53 Octa-core CPU with a maximum clock speed of 2.4GHz. It also has a more powerful Mali-G52 GPU and 4GB or 2GB of DDR4 RAM. The Raspberry Pi 4, on the other hand, is powered by a Broadcom BCM2711 SoC, which is a quad-core ARM Cortex-A72 CPU with a maximum clock speed of 1.5GHz. It has a Broadcom VideoCore VI GPU and either 8GB, 4GB, 2GB, or 1GB of LPDDR4 SDRAM.
Benchmark tests have shown that the ODROID-N2+ performs better in tasks that require heavy processing power, such as 3D rendering, video transcoding, and machine learning. It can also handle multiple tasks simultaneously without any noticeable lag.
The Raspberry Pi 4, however, performs well in tasks that require moderate processing power, such as web browsing, running office applications, and playing retro games. It also has better software support and a larger developer community, making it an excellent choice for beginners and hobbyists who want to explore the world of SBCs.
2. Memory
The ODROID-N2+ and Raspberry Pi 4 have different memory configurations.
The ODROID-N2+ comes with either 4GB or 2GB of DDR4 RAM, which is faster and more power-efficient than the LPDDR4 SDRAM used in the Raspberry Pi 4. The faster RAM can improve overall system performance and reduce power consumption.
In contrast, the Raspberry Pi 4 comes with up to 8GB of LPDDR4 SDRAM, which is a lower power consumption type of RAM. However, the faster DDR4 RAM used in the ODROID-N2+ can offer better performance in memory-intensive tasks, such as running multiple applications or large data processing.
It’s worth noting that the memory capacity and type can affect the price of the board, with the ODROID-N2+ being slightly more expensive than the Raspberry Pi 4 due to its faster DDR4 RAM.
3. Connectivity
The ODROID-N2+ has 4 USB 3.0 ports, a Gigabit Ethernet port, an HDMI 2.0 port, a microSD card slot, and an eMMC module socket. It also has an IR receiver, a 40-pin GPIO header, and a UART serial port. In addition, it has built-in support for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, with an optional antenna kit available for improved wireless connectivity.
The Raspberry Pi 4, on the other hand, has 2 USB 3.0 ports, 2 USB 2.0 ports, a Gigabit Ethernet port, 2 micro-HDMI ports, a microSD card slot, and a 40-pin GPIO header. It also has built-in support for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, with an optional antenna kit available for improved wireless connectivity.
Both SBCs offer similar connectivity options in terms of USB ports, Ethernet, and wireless connectivity. However, the ODROID-N2+ has an HDMI 2.0 port, which supports 4K video output at 60Hz, whereas the Raspberry Pi 4 has two micro-HDMI ports, which support 4K video output at 30Hz.
The GPIO header on both boards allows for easy connection of sensors, motors, and other peripherals, but the ODROID-N2+ has a UART serial port, which can be useful for connecting to certain devices, such as GPS modules and sensors.
In terms of connectivity, both SBCs offer a good range of ports and interfaces, but the ODROID-N2+ offers faster video output and a UART serial port, while the Raspberry Pi 4 offers an additional 2 USB 2.0 ports. The choice between the two will depend on your specific project requirements and peripherals.
4. Price
When it comes to price, the Raspberry Pi 4 is significantly cheaper than the ODROID-N2+. The Raspberry Pi 4 starts at $35 for the 2GB version, while the ODROID-N2+ starts at $69 for the 2GB version. However, it is worth noting that the ODROID-N2+ does come with more powerful hardware, which justifies the higher price.
5. Software Support
Both the ODROID-N2+ and the Raspberry Pi 4 have a large community of developers and users, which means that there is a wealth of resources available online for both SBCs. However, the Raspberry Pi 4 has a larger community than the ODROID-N2+, which means that there are more tutorials, projects, and software available for the Raspberry Pi 4. Additionally, the Raspberry Pi Foundation provides an official operating system called Raspberry Pi OS, which is based on Debian and is optimized for Raspberry Pi. The ODROID-N2+ also has an official Ubuntu-based operating system, which is maintained by Hardkernel.
6. Form Factor
The ODROID-N2+ measures 90 x 90 mm (3.54 x 3.54 inches), which makes it larger than the Raspberry Pi 4, which measures 88 x 58 mm (3.46 x 2.28 inches). However, the difference in size is not significant, and both SBCs are still small enough to fit into compact enclosures or used in portable projects.
Additionally, both SBCs have similar mounting holes, which means that they can be used with the same cases and accessories. However, the size difference could be a deciding factor for some users, depending on their specific project requirements.
7. Power Consumption
When it comes to power consumption, there is a significant difference between the ODROID-N2+ and the Raspberry Pi 4.
The ODROID-N2+ has a power consumption range of 1.6 to 6.2 watts, depending on the workload, which is relatively low for a powerful SBC. The Raspberry Pi 4, on the other hand, has a higher power consumption range of 2.7 to 6.4 watts, depending on the model and workload.
While both SBCs consume relatively low power compared to a traditional desktop computer, the ODROID-N2+ is slightly more power-efficient than the Raspberry Pi 4, making it an excellent choice for projects that require long battery life or low power consumption, such as portable media centers or IoT devices.
Which SBC is Right for You?
In conclusion, both the ODROID-N2+ and the Raspberry Pi 4 are powerful SBCs that can handle a wide range of tasks. If you are looking for a more powerful SBC that can handle tasks such as video editing or machine learning, the ODROID-N2+ may be the better choice for you, but be prepared to pay a higher price.
On the other hand, if you are looking for a cheaper SBC that can handle tasks such as gaming or running multiple virtual machines, the Raspberry Pi 4 may be the better choice for you. Additionally, the Raspberry Pi 4 has a larger community and more software available, which can be a deciding factor for some users.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the choice between the ODROID-N2+ and the Raspberry Pi 4 depends on your specific needs and budget. Both SBCs are great choices for hobbyists, developers, and anyone interested in learning more about computing and programming. With the right setup and software, both SBCs can be used to build a wide range of projects, from media centers to home automation systems.
